Your Cart is Empty
Oxygen therapy is an effective, science-backed tool used to treat various conditions. It can be used for both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Oxygen therapy is often used when oxygen levels in the body are too low, such as when people are exposed to prolonged stress and the body gets into “fight or flight” mode. In some cases, supplemental oxygen therapy – such as recreational oxygen chambers, concentrators or canisters – can be a helpful tool to help rejuvenate the mind and body.
The two main delivery methods of oxygen therapy are:

Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), is a high-flow oxygen therapy which involves breathing ~100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber. The pressure increases the amount of oxygen delivered to cells and tissues throughout the body. It is often used to treat conditions such as carbon monoxide poisoning, decompression sickness, wounds that won’t heal, and infections that don’t respond to antibiotics. In recent years HBOT has been increasingly used in a more recreation setting at lower pressures than medical HBOT chambers, to help the recovery process following vigorous exercise.
Myriad studies have found HBOT can help reduce the effects of certain types of brain injuries in stroke patients, improve recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI), and reduce inflammation and pain associated with conditions like multiple sclerosis and fibromyalgia.
Although hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be beneficial in certain circumstances, there are some risks associated with the treatment. These include ear and sinus pain, vertigo, seizure, vision changes, lung collapse and nausea. It is important to discuss potential risks with your doctor or medical professional before beginning HBOT, and to always have someone guiding you when using hyperbaric oxygen therapy or equipment.
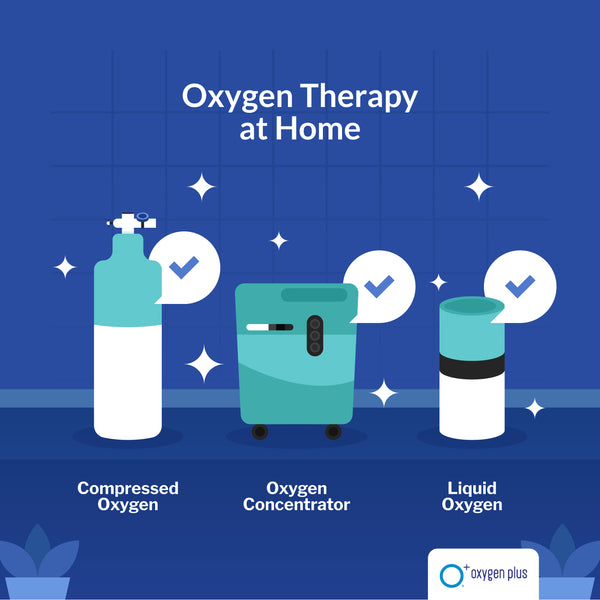
Supplemental oxygen therapy – such as a concentrator or generator prescribed by a doctor – as well as lower pressure oxygen chambers that are available without a doctor or a prescription – are becoming increasingly popular, as it is more affordable and easier to use than high-pressure hyperbaric oxygen chambers. Supplemental oxygen can be delivered through a mask or nasal cannula, and is often delivered at slightly lower oxygen concentrations and pressure than medical HBOT. Designed to help improve daily movement at home and when on the go, supplemental oxygen therapy is used to treat conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Oxygen therapy is typically prescribed for individuals who have difficulty breathing on their own. This can include those with chronic lung diseases, such as COPD and cystic fibrosis, or those who have suffered from a stroke, heart attack, or trauma that has decreased their ability to take in oxygen. It is also used to treat people with low levels of oxygen in their blood, a condition known as hypoxemia.
The use of supplemental oxygen is not limited to people diagnosed with a condition, but can also be used recreationally – as both a recreational oxygen generator or concentrator or handheld oxygen canisters. Oxygen Plus customers report an increased intake of oxygen, delivered through inhaling pure recreational oxygen in portable canisters, helps them focus better at work and perform better during exercise and sports practice – and, with no side effects.
Oxygen therapy helps increase the levels of oxygen in the body, allowing it to better use oxygen for energy and cellular functions. It can also help reduce inflammation, improve blood flow, and activate immune system responses that can fight off infections. Studies have found that a decrease in oxygen levels is associated with an increase in mortality rates, highlighting the importance of understanding how oxygen impacts overall health and wellness, and how it is possible to increase depleted oxygen levels to normal, healthy levels through therapies like HBOT or supplemental oxygen.
A healthy oxygen level is typically between 75–100 mm Hg, or 95–100% SpO2 when measured by a pulse oximeter. If optimal oxygen saturation is a desired goal, it would be important to monitor your oxygen levels with an oximeter at different points of your day to ensure SpO2 levels are at the desired level of optimum health and functioning.
When oxygen levels drop below normal, healthy levels, the mind and body can be impacted – and feelings of sluggishness can appear. If oxygen levels drop significantly low, a dangerous medical condition called hypoxia can occur. Symptoms of hypoxia can include:
It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect you or someone else is experiencing hypoxia.
If you’re an active, healthy person, recreational or sports oxygen may be the form of supplemental oxygen that best fits your oxygen restoration needs. Offering a portable, non-prescription form of supplemental oxygen, Oxygen Plus (O+) lets you enjoy the energy and recovery benefits of breathing pure oxygen anytime, anywhere – without the side effects of other energy supplements, drinks or shots. Keep the O+ Biggi at home to ensure you can breathe pure oxygen whenever you’re feeling tired due to depleted oxygen levels – so you can always think, feel and perform your best.
